



Assignment: (Understand only)
-
Understand the different measurements which may be encountered when purchasing a processor or computer.
- The socket/slot- This is the actual physical mechanism which the CPU fits into, usually it is a zero insertion force or ZIF socket. Some common slots are: Slot 1 (Pentium 2 and 3) and Slot A (AMD Classic Athlon). Some common Sockets are Socket 370 (Pentium 3), Socket 423 (early P4), Socket 478 (Current P4), and Socket 462 (New AMD's)
- Core name- This includes the actual structure of the processor, and how it is built.
- Process size- this indicates the average size of the transistors on the die.
- FSB Speed- this links the processor to the rest of the system, including the Memory (RAM) and peripherals
- Cache- this represents the amount of data which can be stored on the processor for quick access.
- Processor speed- this can be measured in MHz (megahertz), or GHz (gigahertz (1000 MHz)
- A list of all significant processors is listed in the THG article on processors, there is also a comparison sheet of all of those.
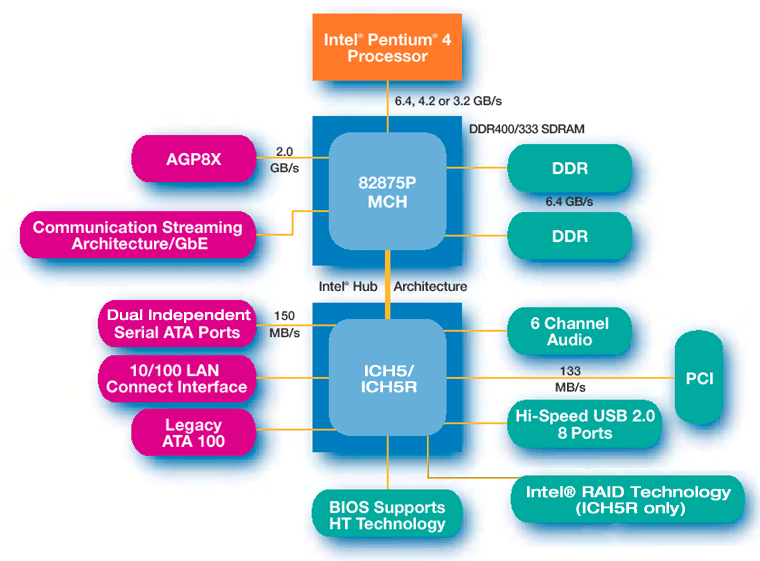
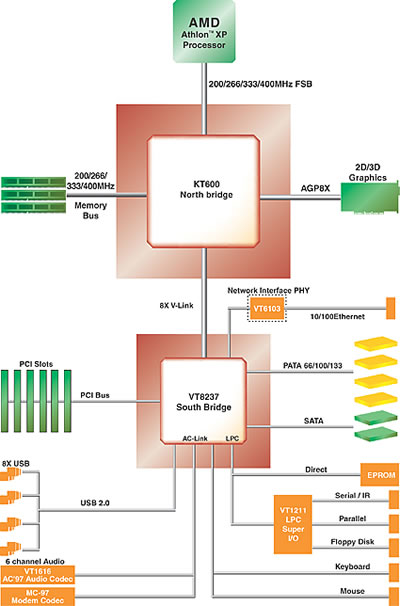
- All of these components are summed up in the following pictures:
- For a summary of Intel chipsets click on the following links: (Requires Adobe Acrobat)